Prometheus Client
In a normal prometheus setup we will find prometheus agents which query configured endpoints at regular intervals. The endpoints are HTTP endpoints serving the current metric state in an encoding defined by prometheus .
ZMX provides the Prometheus encoding for the captured metrics out of the box. To avoid enforcing a particular HTTP implementation, an instrumented application needs to expose the encoded format as an endpoint with the HTTP server of it´s choice.
ZMX Metrics in Prometheus
Most of the ZMX metrics have a direct representation in the Prometheus encoding.
Counter
A counter is represented as a prometheus counter.
# TYPE countAll counter
# HELP countAll
countAll 460.0 1623586224730
Gauge
A gauge is represented as a prometheus gauge.
# TYPE adjustGauge gauge
# HELP adjustGauge
adjustGauge -1.2485836762095701 1623586224730
Histogram
A histogram is represented as a prometheus histogram.
# TYPE zmxHistogram histogram
# HELP zmxHistogram
zmxHistogram{le="0.0"} 0.0 1623586224730
zmxHistogram{le="10.0"} 8.0 1623586224730
zmxHistogram{le="20.0"} 18.0 1623586224730
zmxHistogram{le="30.0"} 30.0 1623586224730
zmxHistogram{le="40.0"} 44.0 1623586224730
zmxHistogram{le="50.0"} 51.0 1623586224730
zmxHistogram{le="60.0"} 59.0 1623586224730
zmxHistogram{le="70.0"} 65.0 1623586224730
zmxHistogram{le="80.0"} 76.0 1623586224730
zmxHistogram{le="90.0"} 88.0 1623586224730
zmxHistogram{le="100.0"} 95.0 1623586224730
zmxHistogram{le="+Inf"} 115.0 1623586224730
zmxHistogram_sum 6828.578655207023 1623586224730
zmxHistogram_count 115.0 1623586224730
Summary
A histogram is represented as a prometheus summary.
# TYPE mySummary summary
# HELP mySummary
mySummary{quantile="0.1",error="0.03"} 147.0 1623589839194
mySummary{quantile="0.5",error="0.03"} 286.0 1623589839194
mySummary{quantile="0.9",error="0.03"} 470.0 1623589839194
mySummary_sum 42582.0 1623589839194
mySummary_count 139.0 1623589839194
Set
A set is represented by a set of prometheus counters, distinguished from each other with an extra label as configured in the aspect.
# TYPE mySet counter
# HELP mySet
mySet{token="myKey-17"} 7.0 1623589839194
mySet{token="myKey-18"} 9.0 1623589839194
mySet{token="myKey-19"} 12.0 1623589839194
mySet{token="myKey-13"} 6.0 1623589839194
mySet{token="myKey-14"} 4.0 1623589839194
mySet{token="myKey-15"} 6.0 1623589839194
mySet{token="myKey-16"} 5.0 1623589839194
mySet{token="myKey-10"} 10.0 1623589839194
mySet{token="myKey-11"} 1.0 1623589839194
mySet{token="myKey-12"} 10.0 1623589839194
Serving Prometheus metrics
ZMX provides a prometheus client that can be used to produce the prometheus encoded metric state
upon request. The state is encoded in the Prometheus case class and the single attribute of
type String holds the prometheus encoded metric state.
So, to retrieve the prometheus encoded state, the application can simply use
val encoded = PrometheusClient.snapshot
val content = encoded.map(_.value)
In our example application we use zio-http to serve the metrics. Other application might choose another HTTP server framework if required.
private lazy val indexPage = HttpData.CompleteData(
Chunk
.fromArray("""<html>
|<title>Simple Server</title>
|<body>
|<p><a href="/metrics">Metrics</a></p>
|<p><a href="/json">Json</a></p>
|</body
|</html>""".stripMargin.getBytes)
)
private lazy val static =
Http.collect[Request] { case Method.GET -> Root => Response.http[Any, Nothing](content = indexPage) }
private lazy val httpEffect = Http.collectM[Request] {
case Method.GET -> Root / "metrics" =>
PrometheusClient.snapshot.map { case Prometheus(value) => Response.text(value) }
}
Now, using the HTTP server and the instrumentation examples we can create an effect that simply runs the sample effects with their instrumentation until the user presses any key.
private lazy val execute =
(for {
s <- ((Server.port(8080) ++ Server.app(static +++ httpEffect)).start *> ZIO.never).forkDaemon
p <- instrumentedSample.program.fork
_ <- putStrLn("Press Any Key to stop the demo server") *> getStrLn.catchAll(_ =>
ZIO.none
) *> p.interrupt *> s.interrupt
} yield ExitCode.success).orDie
Finally, within a ZIO.App we can override the run method, which is now simply the execute
method with a Prometheus client provided in it´s environment:
def run(args: List[String]): URIO[ZEnv, ExitCode] =
execute.provideCustomLayer(
PrometheusClient.live ++ ServerChannelFactory.auto ++ EventLoopGroup.auto(5)
)
Running the prometheus example
Any of the examples can be run from a command line within the ZMX checkout directory with
sbt examples/run
Out of the choices, select the option corresponding to zio.zmx.PrometheusInstrumentedApp.
If everything works, we should be able to use a web browser to go to http://localhost:8080/metrics and should see something like
# TYPE myCounter counter
# HELP myCounter
myCounter{effect="count2"} 46.0 1608982756235
# TYPE setGauge gauge
# HELP setGauge
setGauge 8.66004641453435 1608982756235
# TYPE changeGauge gauge
# HELP changeGauge
changeGauge 90.7178906485008 1608982756235
# TYPE myCounter counter
# HELP myCounter
myCounter{effect="count1"} 92.0 1608982756235
Once we see the metrics being served from our example, we can set up Prometheus and Grafana to create a simple dashboard displaying our metrics.
Simple Prometheus setup
The following steps have been tested on Ubuntu 18.04 running inside the Windows Subsystem for Linux. Essentially, you need to download the prometheus binaries for your environment and start the server with our sample configuration located at
${PROJECT_HOME}/examples/prometheus/promcfg.yml
This will just configure a prometheus job that regular polls http://localhost:8080/metrics for prometheus
encoded metrics.
In addition, you need to download the Grafana binaries for your installation, start the Grafana server and configure prometheus as a single data source.
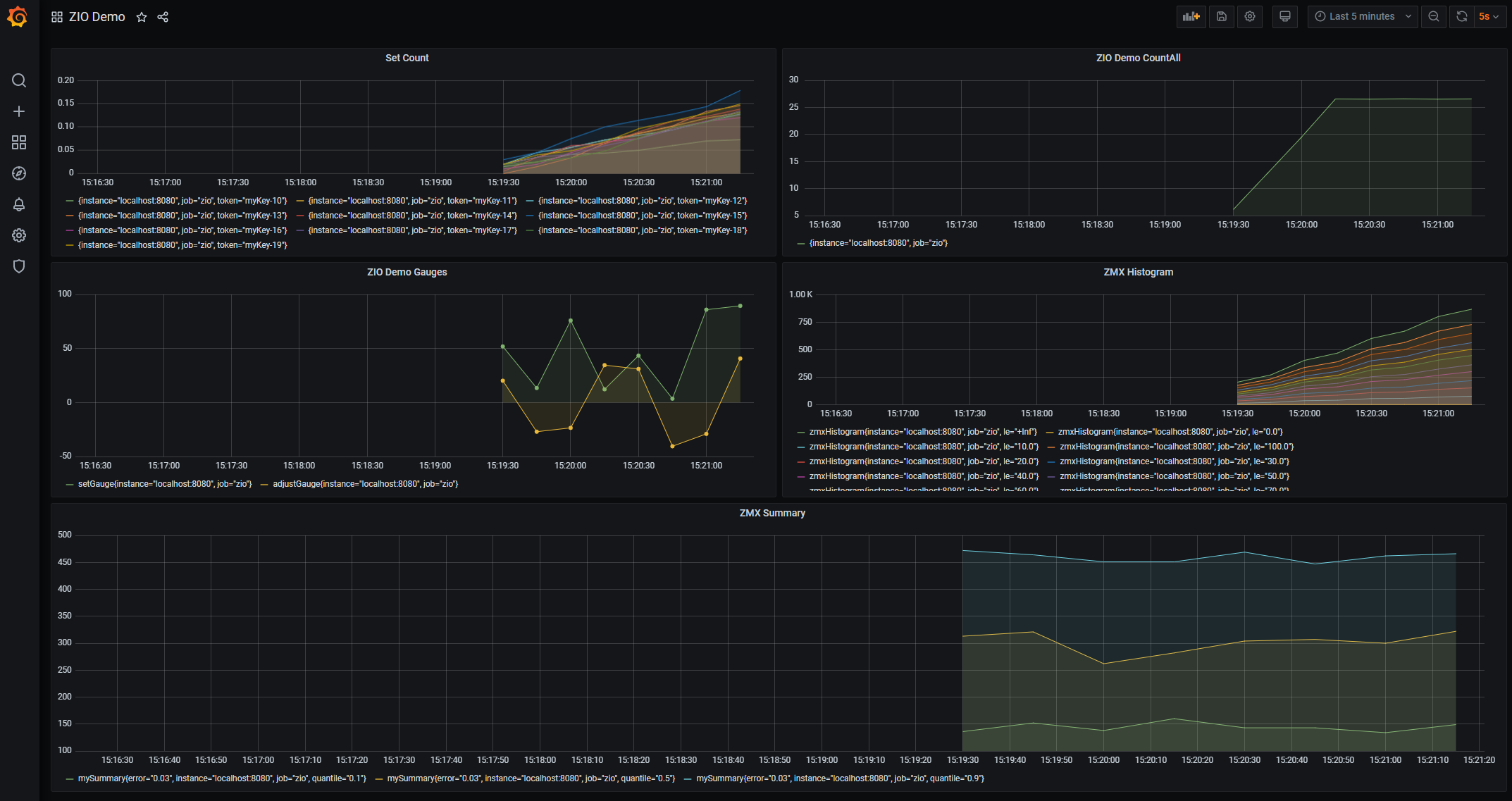
Finally, you can import our example dashboard at examples/prometheus/ZmxDashboard.json and enjoy the results.
These steps are not intended to replace the Prometheus or Grafana documentation. Please refer to their web sites for guidelines towards a more sophisticated setup or an installation on different platforms.
Download and configure Prometheus
In the steps below the ZMX checkout directory will be referred to as $ZMXDIR.
- Download prometheus
- Extract the downloaded archive to a directory of your choice, this will be referred to as
$PROMDIR. - Within
$PROMDIRexecute./prometheus --config.file $ZMXDIR/examples/prometheus/promcfg.yml
Download and configure Grafana
Download grafana
Extract the downloaded archive to a directory of your choice, this will be referred to as
$GRAFANADIR.Within
$GRAFANADIRexecute./bin/grafana-serverThis will start a the Grafana server.
Now you should be able to login to Grafana at
http://localhost:3000' with the default useradminwith the default passwordadmin`.Upon the first login you will be asked to change the default password.
Within the Grafana menu on the left hand side you will find
Manage Dashboardswithin that page, selectImport.You can now either install a dashboard from grafana.com or use a text field to paste JSON.
Paste the content of
$ZMXDIR/examples/prometheus/ZmxDashboard.jsoninto the text field and selectLoad.This will import our dashboard example.
Now, under
Manage Dashboardsthe just imported ZIO dashboard should be visible.Navigate to the dashboard.
Grafana dashboard
Here is a screenshot of the Grafana dashboard produced with the setup above.